
/sodium-chloride-structure-artwork-160936423-589330f15f9b5874eea7ba04.jpg)
Thus the predominantly ionic nature of a phase cannot safely be inferred either from crystal structure or from calculated lattice energies since many metallic alloys adopt the NaCl-type or CsCl-type structures (e.g. There is a lively controversy concerning the interpretation of these and other properties, and cogent arguments have been advanced both for the presence of hydride ions H" and for the presence of protons H+ in the d-block and f- block hydride phases.These difficulties emphasize again the problems attending any classification based on presumed bond type, and a phenomenological approach which describes the observed properties is a sounder initial basis for discussion. The data are summarised below (standard enthalpies in kJ).
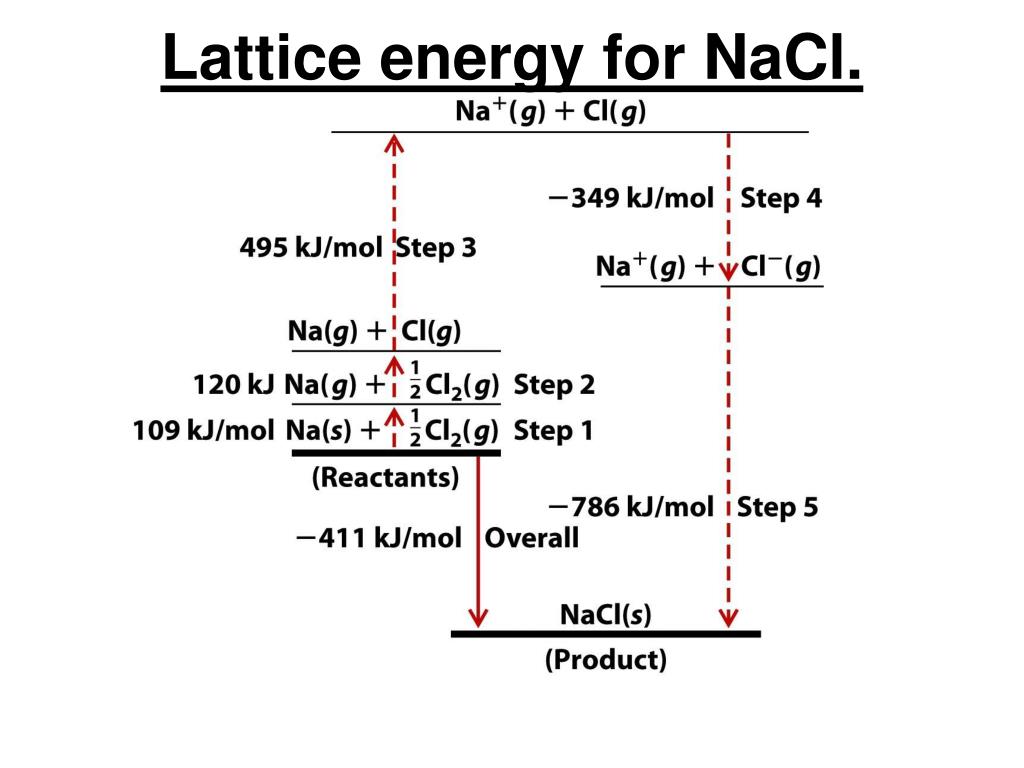
The lattice energy is calculated on the assumption that the compound is ionic and that Na is comparable in size with Mg ". The energy diagram for the formation of this hypothetical compound follows the pattern of that for NaCl but an additional endothermic step is added for the second ionisation energy of sodium. Let us consider the formation of a number of possible ionic compounds and first, the formation of sodium dichloride, NaCl2. We therefore need to examine the evidence provided by energetic data. 354) we cannot rely fully on this theory. However, since some noble gas atoms can lose electrons to form cations (p.
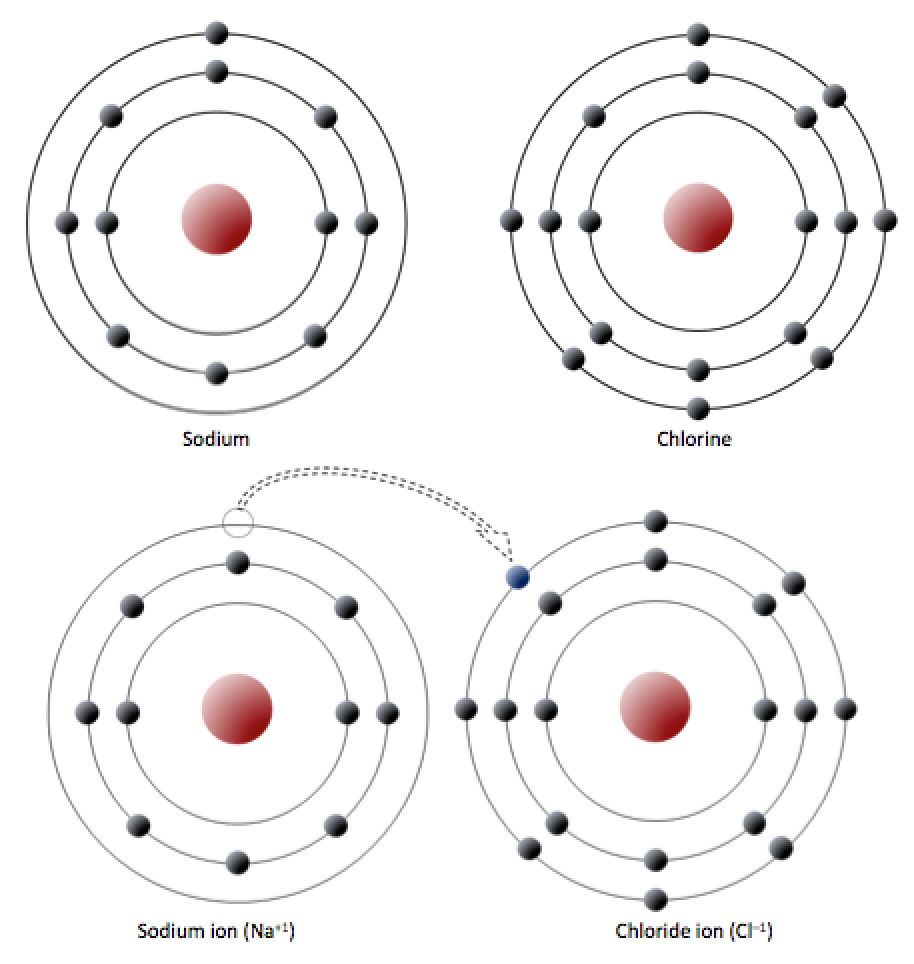
To date there is no evidence that sodium forms any chloride other than NaCl indeed the electronic theory of valency predicts that Na" and CU, with their noble gas configurations, are likely to be the most stable ionic species. Commonly used to calculate lattice energies of ionic solids and average bond energies of covalent compounds. NaCl lattice energy Born-Haber cycle A thermodynamic cycle derived by application of Hess s law.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
